BIOLOGY
INTRODUCTION
The study of biology in ninth grade will give an approach to life understanding by studying specific process related to metabolism, interactions with the environment and wider concepts as reproduction and mendelian genetics. These contents will be related to wider concepts as systems, relationships and change.
GENERAL OBJECTIVE
To construct a proper comprehension about the importance of metabolism in maintaining life through mechanism as homeostasis, movement and transport, diffusion, osmosis, gas interchange and circulation at the same time enable student to comprehend his relationship with the world mediated by the nervous system, hormones and receptors.
At the end of the first semester the student should be able to use different sources of information to get a good understanding of scientific information related to those phenomena and can research in new topics of his interest.
COMPETENCES / ABILITIES TO DEVELOP
Objective A: Knowing and understanding
i. explain scientific knowledge.
ii. apply scientific knowledge and understanding to solve problems set in familiar and unfamiliar situations.
iii. analyze and evaluate information to make scientifically supported judgments.
Objective B: Inquiring and designing
i. explain a problem or question to be tested by a scientific investigation.
ii. formulate a testable hypothesis and explain it using scientific reasoning.
iii. explain how to manipulate the variables, and explain how data will be collected.
iv. design scientific investigations.
Objective C: Processing and evaluating
i. present collected and transformed data.
ii. interpret data and explain results using scientific reasoning.
iii. evaluate the validity of a hypothesis based on the outcome of the scientific investigation.
iv. evaluate the validity of the method.
v. explain improvements or extensions to the method.
Objective D: Reflecting on the impact of science
i. explain the ways in which science is applied and used to address a specific problem or issue.
ii. discuss and evaluate the various implications of the use of science and its application in solving a specific problem or issue.
iii. apply scientific language effectively.
iv. document the work of others and sources of information used.
METHODOLOGY
• Team or individual workshops.
• Presentations.
• Individual Tests.
• Team tests’ corrections.
• Experimental activities.
• Whole class discussions.
CONTENT AND CONCEPTS
Metabolism
Digestion as a horizontal process of metabolism
Enzymes
Homeostasis
Movement and transport in cell membrane
Diffusion and osmosis
Gas interchange
Circulation
Interactions with the environment
Nervous system
Receptors
Hormones
Hormones and Receptors
Hormones
Receptors
Body Development
Reproduction
Sexual and asexual reproduction.
Human reproduction.
Sexually transmitted diseases, prevention and care.
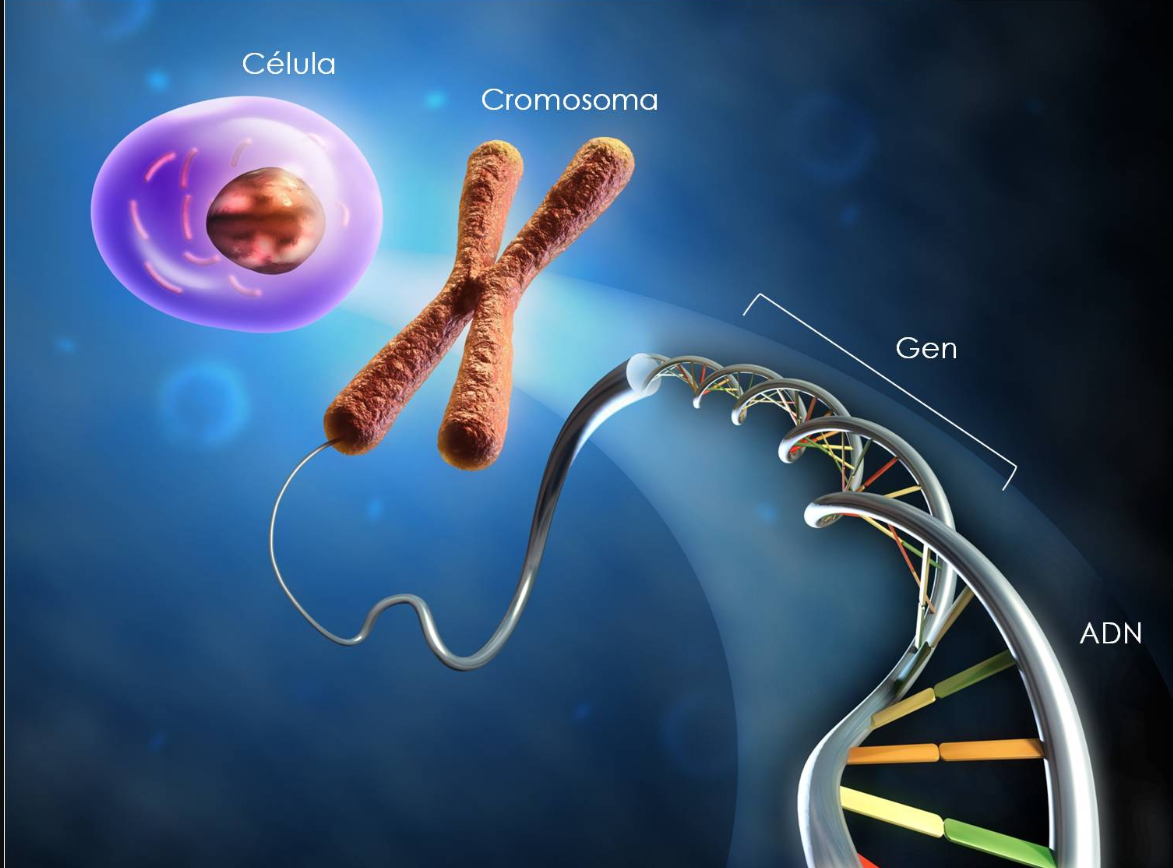
Mendelian genetics
Mendelian and heredity principles.
DNA Replication and transcription.
Gene expression, mutations and genetic variability.
EVALUATION PROCESS
Formative evaluation |
|
Summative evaluation |
|
Evaluation Criteria | Percentages |
Knowing and understanding | 25% |
Inquiring and designing | 25% |
Processing and evaluating | 25% |
Reflecting on the impact of science | 25% |
- Profesor: Katherine Tabares Marin